EPSS vs. CVSS: Understanding the Differences and Use Cases

Why This Topic Matters
When it comes to prioritizing vulnerabilities, knowing what to fix first is critical—but not all vulnerabilities are created equal. For years, organizations have relied on the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) to assess severity. But as threats evolve and the volume of vulnerabilities grows, many teams are adopting the Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS) to better predict real-world risk.
This blog explains how CVSS and EPSS work, how they differ, and how they can be used together to improve vulnerability remediation decisions.
What Is CVSS? (Common Vulnerability Scoring System)
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a standardized framework developed by FIRST for rating the severity of security vulnerabilities. It provides a numeric score (typically from 0.0 to 10.0) based on static attributes such as:
- Attack vector (e.g., network vs. physical access)
- Complexity of exploitation
- Required privileges and user interaction
- Impact on confidentiality, integrity, and availability
CVSS is widely adopted in vulnerability scanning tools and compliance frameworks. However, it does not account for whether a vulnerability is actively being exploited in the wild.
What Is EPSS? (Exploit Prediction Scoring System)
The Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS), also developed by the Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams (FIRST), predicts the likelihood that a software vulnerability will be exploited in the real world within the next 30 days.
EPSS uses a machine learning model trained on real-world exploit activity and contextual data such as:
- Vulnerability age and publication volume
- Exploit availability (e.g., on GitHub or Metasploit)
- CVSS characteristics
- Network exposure (e.g., Shodan results)
Scores range from 0.0 to 1.0, representing the probability of exploitation.
Key Differences: CVSS vs. EPSS
While both CVSS and EPSS offer numeric scores for evaluating vulnerabilities, they differ fundamentally in purpose and methodology:
| Attribute | CVSS | EPSS |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Severity assessment | Exploit likelihood prediction |
| Score range | 0.0-10.0 | 0.0-1.0 |
| Based on | Static technical details | Machine learning + real-world exploit data |
| Mantained by | FIRST | FIRST (via the EPSS SIG) |
| Update frequency | Periodically | Daily |
| Use case | Baseline severity, compliance | Risk-based priortization |
Why Use Both CVSS and EPSS Together?
Used in isolation, CVSS can overinflate the urgency of vulnerabilities that are not likely to be exploited, while EPSS alone may underrepresent the severity of certain business-critical exposures.
Together, they provide a more complete picture:
- CVSS tells you how bad it *could* be.
- EPSS tells you how likely it *will* be.
This dual scoring approach helps security teams:
- Filter out low-risk vulnerabilities with high CVSS but low EPSS
- Prioritize high-risk vulnerabilities with moderate CVSS but high EPSS
- Justify remediation decisions to business stakeholders
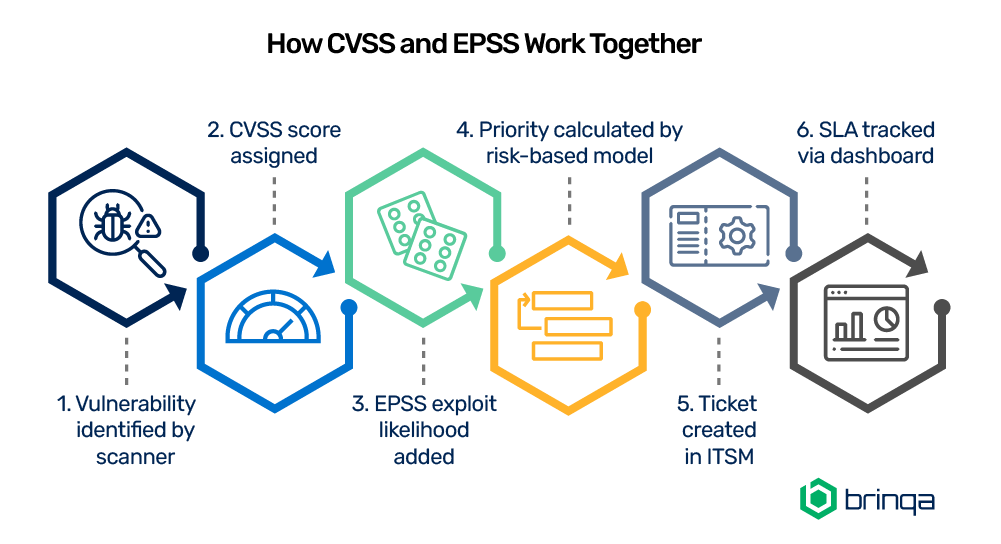
Practical Application: A Risk-Based Prioritization Strategy
Modern vulnerability management platforms integrate both EPSS and CVSS scores into vulnerability risk prioritization logic. This enables teams to:
- Ingest vulnerability data from multiple scanners
- Enrich findings with real-time exploitability intelligence
- Automatically assign remediation tasks based on configurable thresholds
By combining CVSS, EPSS, and business context (such as asset criticality or SLA tiers), organizations can focus remediation efforts where they will have the greatest impact.
How Brinqa Supports EPSS + CVSS in Practice
Brinqa’s Vulnerability and Exposure Management Platform integrates both EPSS and CVSS—two leading vulnerability scoring systems into its prioritization engine, helping our customers:
- Reduce false positives and noise
- Align remediation with risk
- Communicate findings more effectively to business and IT stakeholders
Learn how CVSS and EPSS fit into a broader strategy in our post on Risk-Based Vulnerability Management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does EPSS stand for?
EPSS stands for Exploit Prediction Scoring System. It estimates the probability that a vulnerability will be exploited in the wild.
Is CVSS being replaced by EPSS?
No. CVSS and EPSS serve different purposes. EPSS complements CVSS by adding a predictive risk dimension to severity scores.
How often are EPSS scores updated?
EPSS scores are recalculated and published daily based on new exploit data and model adjustments.
Can CVSS and EPSS be used together?
Yes. In fact, using both scores together leads to smarter, more risk-aligned remediation decisions.
What is the main difference between CVSS and EPSS?
CVSS measures the severity of a vulnerability based on static characteristics, while EPSS predicts the likelihood it will be exploited. CVSS tells you how bad it could be; EPSS tells you how likely it is to happen.
Which is better for vulnerability prioritization: EPSS or CVSS?
EPSS is better for prioritizing based on real-world risk, while CVSS is useful for understanding technical severity and meeting compliance requirements. The most effective programs use both together.
Take the Next Step Toward Smarter Vulnerability Prioritization
Understanding the difference between CVSS and EPSS is a foundational step. The real impact comes when these insights are applied through automation, business context, and continuous risk evaluation.
Brinqa helps security teams:
- Integrate CVSS and EPSS scores into a unified risk model
- Prioritize and automate remediation workflows
- Track performance with real-time dashboards and SLA metrics
To see how Brinqa can help your organization improve vulnerability risk prioritization, request a demo.