Why Risk-Based Vulnerability Management Belongs at the Center of Your CTEM Strategy

Cyber threats evolve by the hour — and traditional vulnerability management practices just can’t keep up. Scanning a network periodically and relying on static risk scores to remediate findings may have worked in the past, but today’s attackers move too fast. That’s where continuous threat exposure management (CTEM) comes in. And at the center of a CTEM strategy? Risk-based vulnerability management that continuously aggregates, prioritizes, and orchestrates remediations.
This post breaks down why risk-based vulnerability management (RBVM) belongs at the heart of a CTEM approach.
What Is Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM)?
Think of CTEM like a smart home security system that never sleeps. It continuously monitors, tests, and improves your organization’s defenses — so you can fix problems before attackers find them.
Rather than focusing solely on compliance or check-the-box scans like vulnerability management of old, CTEM prioritizes exposures based on risk, exploitability, and business impact. It’s about staying ahead, not just catching up.
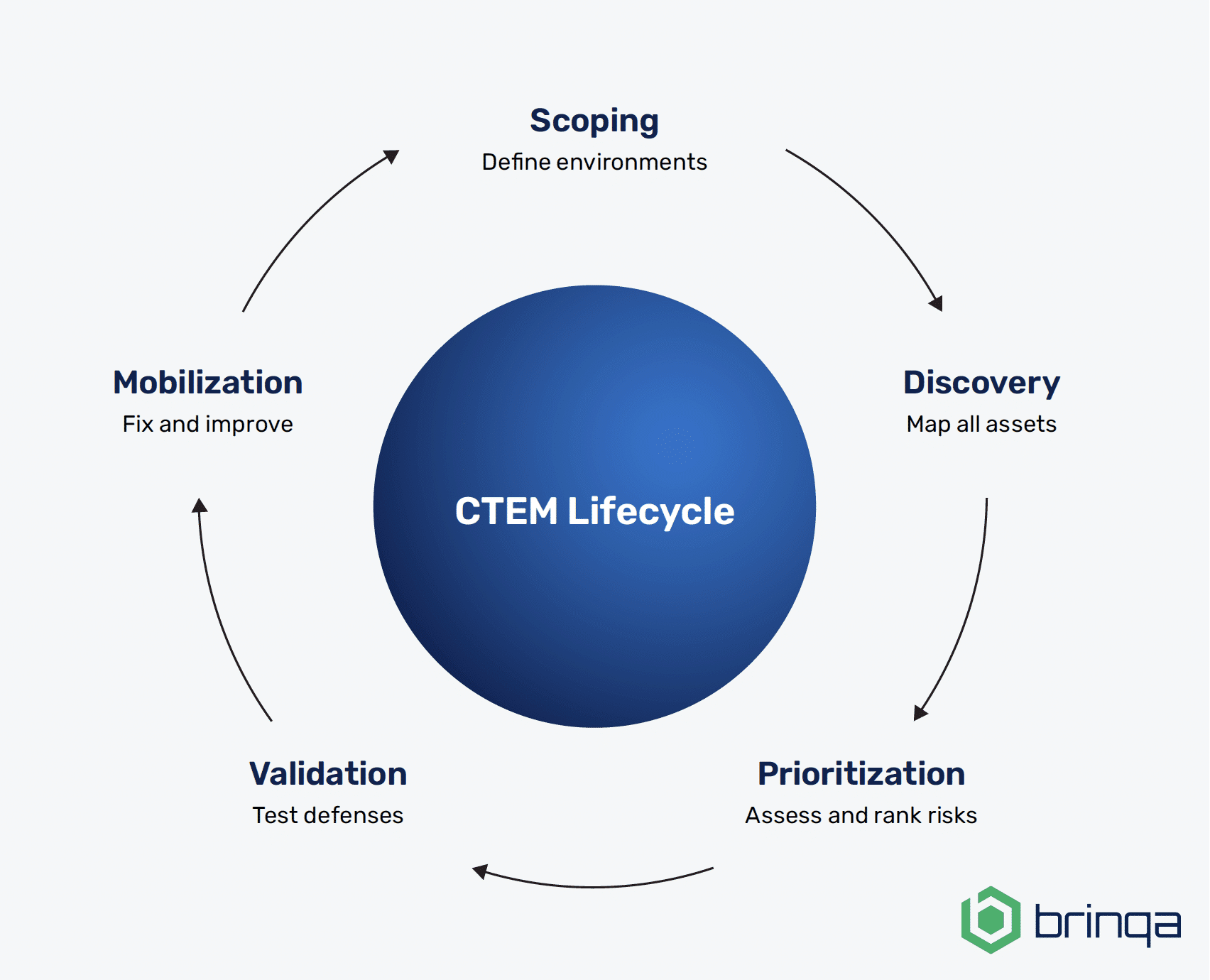
Gartner outlines five key phases of a CTEM program. Here’s how they work — through the lens of our home security system analogy:
- Scoping: Take inventory of what you’re protecting (like your floor plan).
- Discovery: List everything that could be a way in (doors, windows).
- Prioritization: Decide which weaknesses matter most (fix the broken front door before the attic window).
- Validation: Simulate attacks to see what holds up and what breaks down.
- Mobilization: Fix problems and keep improving.
The objective of a CTEM approach is to repeat this process continuously, like a lifecycle.
Tools That Power CTEM (and the Problems a Multi-Tool Approach Creates)
CTEM isn’t a product, it’s an approach that depends on a powerful ecosystem of security tools, including:
- Asset Discovery Tools to map your digital footprint
- Vulnerability Scanners (as well as application security and cloud security-specific tools) to detect weak spots
- Attack Surface Management (ASM) to assess what’s exposed externally
- Threat Intelligence Platforms to track real-world threats
- Breach and Attack Simulation (BAS) to test defenses
- SIEM and SOAR platforms to detect and respond to threats
- RBVM to decide what matters most
CTEM can be a powerful approach, but it’s not plug-and-play. Common roadblocks to implementing a multi-tooled CTEM approach include:
- Too many tools, not enough integration: Those tools we mentioned above often work in silos.
- Incomplete asset visibility: Shadow IT and unmanaged assets remain blind spots.
- Prioritization overload: Static CVSS scores don’t reflect real-world risk.
- Lack of skills and resources: Continuous management takes time and talent.
- High costs: Licensing and infrastructure investments can be steep.
- Resistance to change: Teams may be hesitant to adopt new processes.
Why RBVM is the Star of the CTEM Show
While each CTEM-affiliated tool plays an important role, RBVM sits at the center, connecting the dots among the different data feeds and assets and telling teams what to fix first. After all, without intelligent aggregation and prioritization, security teams are left chasing endless to-do lists. That’s where RBVM shines. Risk-based vulnerability management combines:
- Vulnerability scan data
- Asset context
- Threat intelligence
- Real-time exploitability
- Business impact
…into a single, risk-based score that helps teams act fast and smart. RBVM helps answer the most important question: “Which of these thousands of issues should I fix first to reduce the most risk?”
How to Get CTEM Right
Organizations can overcome the challenges of implementing a CTEM approach with a few smart strategies:
- Start with unifying your organization’s asset inventory — you can’t protect what you don’t see. Consolidate your security toolset using platforms that integrate well.
- Automate repeatable tasks like scanning, patching, and alerting–that means no more spreadsheets to consolidate findings. This will naturally build collaboration between security, IT, and DevOps teams.
- Use RBVM to consolidate asset data, normalize scoring, prioritize fixes, and focus remediation automations on the riskiest exposures.
How Brinqa Powers CTEM
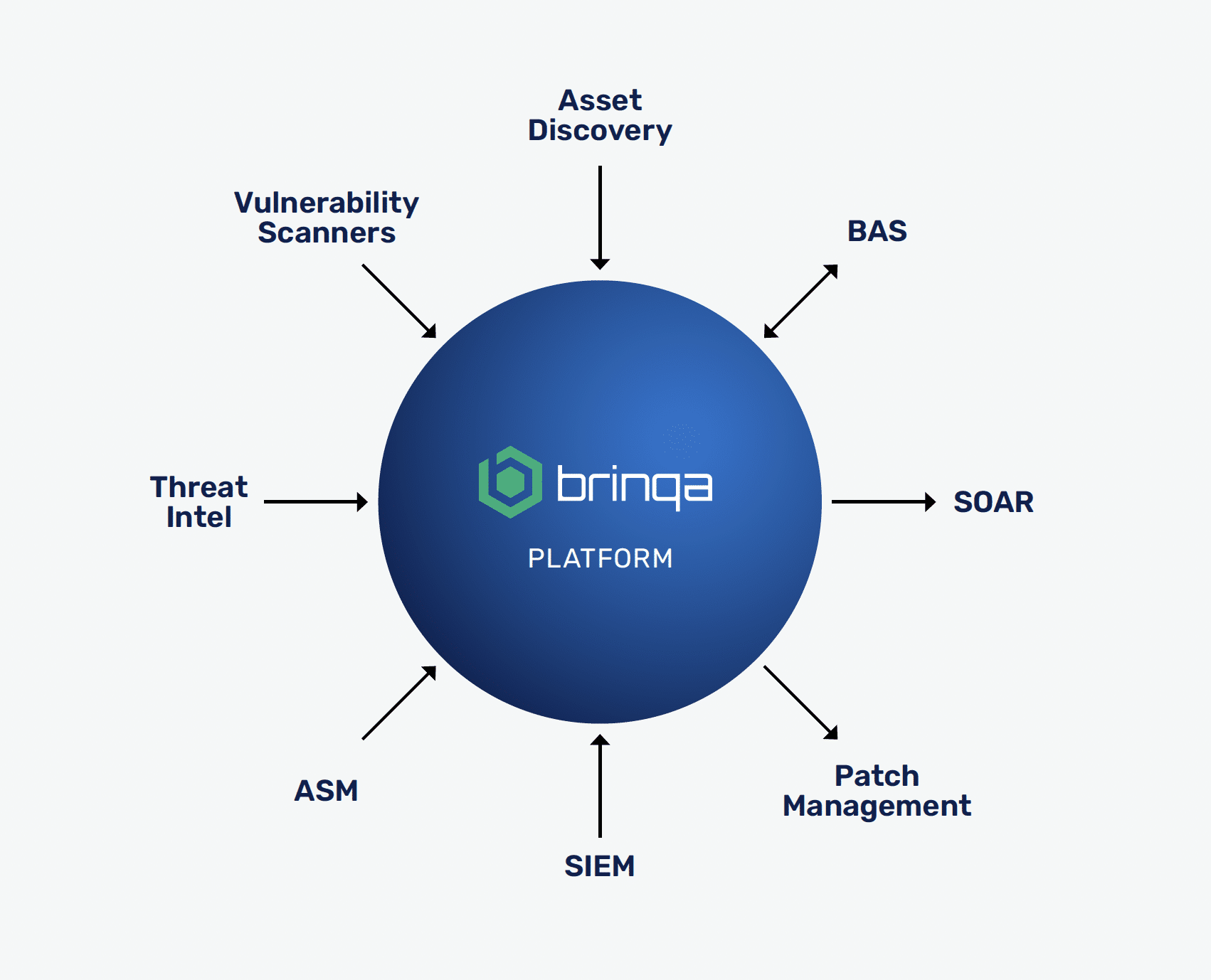
Brinqa is a unified exposure management platform uniquely designed to centralize, prioritize, remediate and report on security findings across your environment. The Brinqa platform connects to over 220 tools, including:
- Asset discovery platforms (like Axonius and ServiceNow)
- Vulnerability scanners (like Qualys, Tenable, and Wiz)
- Threat intelligence feeds (like Recorded Future)
- SIEMs and SOARs (like Cortex)
- BAS tools (like CyCognito)
Brinqa brings it all together to provide a single source of truth and turn insight into action. With Brinqa, companies like Nestlé, SAP, and Cambia have reduced remediation time, uncovered blind spots, and focused on the 2% of issues that posed 98% of risk.
CTEM is the future of cybersecurity defense — but without RBVM, it’s just noise. Put risk-based prioritization at the heart of your CTEM strategy, and you’ll not only reduce risk faster — you’ll make smarter, more cost-effective decisions.
Want to Go Deeper?
Download the new white paper, Why Risk-Based Vulnerability Management Should Be at the Center of Continuous Threat Exposure Management, for a deep-dive into the tools, challenges and approaches for maximizing CTEM success.
For more on how Brinqa can enable a comprehensive CTEM approach, request a demonstration today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between CTEM and traditional vulnerability management?
Traditional vulnerability management often relies on periodic scanning and static risk scores. CTEM is continuous and dynamic — it evaluates exposures in real time based on context, business impact, and real-world threat intelligence.
Why is risk-based vulnerability management (RBVM) essential for CTEM?
RBVM ensures that remediation efforts focus on the most critical vulnerabilities, not just the most numerous. It combines threat intel, asset value, exploitability, and business impact to prioritize what matters most.
What kinds of tools are involved in a CTEM strategy?
A complete CTEM program may include:
- Asset discovery tools
- Vulnerability scanners
- Threat intelligence platforms
- Attack surface management tools
- Breach and attack simulation (BAS)
- SIEM and SOAR platforms
- RBVM platforms (like Brinqa)
What are the biggest challenges to implementing CTEM?
Common obstacles include:
- Tool sprawl and poor integration
- Incomplete visibility of digital assets
- Resource constraints
- Prioritization overload
- High implementation and licensing costs
How does RBVM help reduce alert fatigue?
RBVM cuts through the noise by surfacing only the vulnerabilities that are both exploitable and impactful. It filters out low-priority issues, reducing the volume of alerts security teams need to triage.
How does Brinqa support CTEM and RBVM?
Brinqa integrates with 220+ security tools to centralize, normalize, and prioritize exposure data. It serves as a control center for CTEM—automating prioritization, orchestration, and remediation workflows at enterprise scale.
What’s the business value of investing in a CTEM approach with RBVM?
Organizations that adopt a CTEM approach with RBVM at the center see:
- Faster remediation from automations and centralized orchestration
- Reduced risk of breaches due to comprehensive asset and vulnerability management
- Lower operational costs through automations
- Better use of security resources through prioritization
- Alignment of security with business priorities from consolidated reporting




