How to Prioritize Vulnerabilities: A Modern Guide to Risk-Based Remediation
by Brad Hibbert, COO & CSO//12 min read/

Security teams at large enterprises face an overwhelming volume of vulnerabilities across global infrastructure and hybrid environments. Yet not all risks are equal, and treating them as such can drain resources and leave critical systems exposed. Effective vulnerability prioritization is essential for managing cyber risk at scale and ensuring that remediation efforts are aligned with business impact and threat context.
In this guide, we’ll break down what vulnerability prioritization means today, the frameworks and signals that matter most, and how a modern, risk-based approach can help security teams focus on what truly matters.
What Is Vulnerability Prioritization?
Vulnerability prioritization is the process of determining which vulnerabilities should be addressed first based on their potential impact on the organization. It goes beyond severity scores to account for exploitability, asset importance, threat activity, and business impact—ensuring limited resources are directed toward the vulnerabilities that pose the greatest actual risk.
Why Prioritization Matters for Large Enterprises
In 2024 alone, tens of thousands of vulnerabilities were publicly disclosed—a number that continues to rise year over year. For large enterprises managing thousands of assets across hybrid environments, the volume is overwhelming. Compounding the challenge, vulnerability data is fragmented, remediation teams are stretched thin, and audit expectations are rising.
The reality is that only a small fraction of vulnerabilities are ever exploited—Qualys found just 0.91% were considered weaponized in early 2024, meaning they had known exploits, were used in ransomware or malware, or were actively exploited in the wild (source). But those few represent the most urgent and damaging threats.
Prioritization is how security leaders cut through the noise, reduce exposure, and ensure teams are focused on what truly matters. It’s essential not just for reducing cyber risk, but for demonstrating accountability to executives and regulators, and for keeping overstretched security and IT teams focused and effective.
Effective prioritization is not just about efficiency—it’s about survival. By focusing on the vulnerabilities most likely to be exploited and most damaging to the business, security leaders can reduce attack surface, demonstrate accountability to executives and regulators, and prevent burnout across security and IT teams.
Traditional Approaches (and Why They Fall Short)
Historically, security teams have used methods such as:
- CVSS Scores: Static severity ratings that lack context.
- Manual Triage: Resource-intensive and inconsistent.
- Vulnerability Prioritization Matrices: Simple scoring grids that often fail to scale.
These approaches can be helpful starting points but often miss critical dimensions like real-world exploitability and business relevance. At enterprise scale, these gaps result in mounting vulnerability backlogs, wasted effort, and missed risk signals.
A Risk-Based Vulnerability Prioritization Framework
Modern security programs use a risk-based approach that contextualizes vulnerabilities across multiple dimensions:
- Asset Criticality – How important is the affected system to business operations?
- Threat Intelligence – Are threat actors actively exploiting this vulnerability in the wild?
- Exploitability Signals – Is there known exploit code? What’s the EPSS (Exploit Prediction Scoring System) score?
- Business Context – Who owns the system? What data does it process? Is it tied to a revenue-generating function?
- Exposure Context – Is the asset exposed to the internet or only accessible internally?
- Security Controls – Are compensating controls in place to mitigate the risk?
This framework enables enterprise teams to align vulnerability remediation efforts with the organization’s risk appetite and compliance requirements. Explore the full methodology in our risk-based vulnerability management guide.
How to Prioritize Vulnerabilities for Remediation: A Step-by-Step Approach
- Consolidate Vulnerability Data: Unify findings across scanners, cloud platforms, asset inventories, CMDBs, and pen testing tools. Large enterprises often deal with fragmented data sources—normalizing and reconciling this data is essential to gain full visibility.
- Enrich With Context: Add business metadata, ownership, and environment details to each finding. For example, identifying whether an asset supports a customer-facing product line or internal HR system adds vital prioritization context.
- Incorporate Threat and Exploit Intelligence: Use feeds like CISA KEV, EPSS, and commercial intel sources to gauge real-world risk. For a deeper dive on these scoring systems, see our post on EPSS vs. CVSS. EPSS can help focus on the vulnerabilities most likely to be exploited soon.
- Score Based on Risk: Use a dynamic, configurable scoring model that weights business impact, exploitability, and exposure. Enterprise teams may need different scoring logic by business unit or region.
- Review Security Controls: Evaluate whether existing controls—like endpoint detection, segmentation, or web application firewalls—meaningfully reduce risk. A vulnerability may be deprioritized if strong, layered controls already mitigate it.
- Estimate Remediation Effort: Factor in the time, complexity, and potential service disruption associated with fixing each vulnerability. For example, patching a business-critical database may require downtime coordination and QA validation.
- Automate Remediation Workflows: Trigger automated ticketing with SLAs, owner assignment, and escalation across IT, DevOps, and AppSec teams. Learn more in our post on automated vulnerability remediation. This reduces reliance on email or spreadsheets and ensures accountability.
- Measure and Refine: Track MTTR, SLA adherence, and false positive rates. Use dashboards to review backlog trends, team performance, and logic effectiveness. Continuously optimize for scale and accuracy.
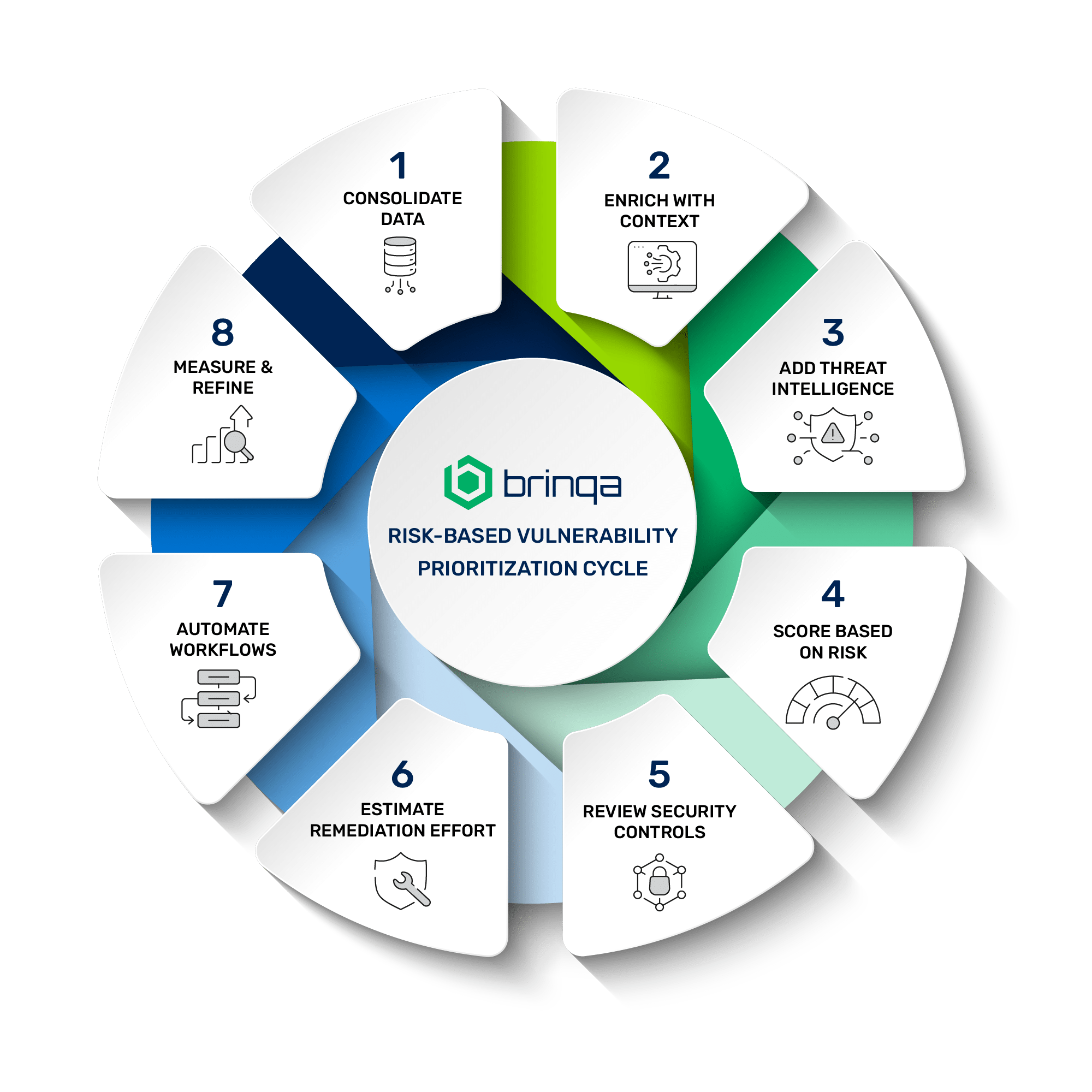
This eight-step framework helps enterprise security teams consolidate data, apply context, and operationalize risk-based vulnerability remediation at scale.
Aligning Remediation With Business Objectives
Prioritization isn’t just about technical severity—it must reflect how vulnerabilities affect the business. Aligning remediation to business impact helps ensure security efforts drive outcomes executives care about.
Examples of business-aligned prioritization:
- Prioritize vulnerabilities on systems tied to revenue, regulatory compliance, or customer trust (e.g., payment platforms, data warehouses, healthcare apps).
- Deprioritize issues on decommissioned systems, developer sandboxes, or assets isolated by design.
- Balance urgency against remediation effort, availability requirements, and stakeholder coordination.
When prioritization reflects enterprise business goals, it’s easier to justify remediation work, meet audit expectations, and foster trust between security and business teams.
Sample Vulnerability Prioritization Logic Table
| Condition | Priority Level |
|---|---|
Critical asset + known exploit | High |
Internet-facing + high EPSS score | High |
End-of-life software with no patch | Medium |
Internal-only + low impact + no known exploit | Low |
Enterprise Challenges in Vulnerability Prioritization
Managing vulnerability prioritization at scale introduces unique challenges:
- High Volume and Velocity: The number of new vulnerabilities grows year over year. Teams struggle to triage issues quickly enough.
- Siloed Operations: Coordination between security, IT, cloud, and development teams is often fragmented.
- Resource Constraints: Many teams are understaffed or rely on manual processes that don’t scale.
- Visibility Gaps: Without full visibility into asset inventories and business context, prioritization logic breaks down.
- Accountability Pressure: Regulatory scrutiny and board-level reporting create added urgency and risk if prioritization fails.
Overcoming these challenges requires an integrated platform that can bring together people, data, and processes.
Pitfalls to Avoid
- Relying Solely on CVSS: Lacks exploit and business context.
- Overprioritizing Low-Risk Issues: Drains resources from more critical fixes.
- Static Scoring: Doesn’t adapt to changing environments or new threat intel.
- Lack of Stakeholder Visibility: Makes it harder to justify resource allocation and track effectiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a vulnerability prioritization matrix?
A vulnerability prioritization matrix is a simplified scoring grid that helps teams rank vulnerabilities based on severity and asset importance. While useful as a starting point, it often lacks the depth and scalability of a risk-based approach.
What is the EPSS score and why is it important?
EPSS (Exploit Prediction Scoring System) predicts the likelihood that a vulnerability will be exploited in the wild. It helps teams make informed decisions about which vulnerabilities to fix first based on threat likelihood.
How often should vulnerability prioritization logic be updated?
Prioritization logic should be revisited regularly—ideally quarterly or in response to major changes in infrastructure, business priorities, or threat landscape.
Can Brinqa replace our current scanning tools?
No, Brinqa integrates with your existing scanning tools. It provides the intelligence and workflows needed to make vulnerability data actionable.
How does Brinqa help prioritize remediation?
Brinqa calculates contextual risk scores, maps vulnerabilities to assets and owners, and automates workflows—ensuring the right issues are addressed quickly.
Transforming Prioritization into Action with Brinqa
If you’re leading a vulnerability management program at a large enterprise, you know that scale, context, and coordination are everything. Brinqa helps program leaders get above the noise with unified visibility, risk-based logic, and automated workflows that work across silos. The platform also includes cross-team collaboration features, pre-built reporting templates for compliance frameworks like NIST 800-53 and PCI DSS, and tailored dashboards for executives and auditors.
With our unified vulnerability and exposure management platform, security teams can:
- Unify vulnerability, asset, and threat data across hybrid environments
- Apply configurable risk scoring logic tailored to enterprise priorities
- Automate ticketing, SLA workflows, and remediation processes
- Improve MTTR across thousands of assets with cross-functional collaboration
- Generate executive-ready reports and dashboards for audit and board visibility
Brinqa delivers a centralized, risk-based approach to vulnerability management that scales with your organization and adapts to your unique context. See how Fortune 500 security teams use Brinqa to scale vulnerability remediation: Request a Demo
- What Is Vulnerability Prioritization?
- Why Prioritization Matters for Large Enterprises
- Traditional Approaches (and Why They Fall Short)
- A Risk-Based Vulnerability Prioritization Framework
- How to Prioritize Vulnerabilities for Remediation: A Step-by-Step Approach
- Aligning Remediation With Business Objectives
- Sample Vulnerability Prioritization Logic Table
- Enterprise Challenges in Vulnerability Prioritization
- Pitfalls to Avoid
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Transforming Prioritization into Action with Brinqa


